The objective of the smart city concept is to optimize energy consumption and the use of resources. Opportunities for this arise from networking systems that have acted independently of each other to date.
There are countless examples: The conversion of excess, ecologically generated electrical energy into hydrogen or synthetic natural gas and mixing it into gas grids allows for large quantities of electricity from renewable energies to be stored long-term. Waste hear from industrial plants can be used as utility heat in building heating systems. Energy efficiency in road traffic can be increased using intelligent traffic control systems.
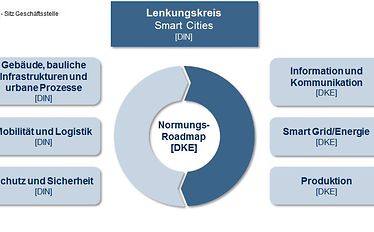
For this reason, it is important to comprehensibly analyze the subsystems of electricity, gas, heat subsystems and other energy sources as an overall energy system in the standardization roadmap and create compatibility.
A smart grid provides many prerequisites to efficiently control and regulate the energy system: A largely automated and self-repairing supply network, smart meter, localized energy generation and interim storage, local energy management, the takeover of network services by smart homes and buildings, bundling small units into virtual power plants and electronic marketplaces for energy and balancing power.
The interaction between the individual stakeholders is particularly important in a smart city. Basic prerequisites include a wide-scale communications infrastructure, interoperability and compatibility of all involved systems. Full consensus standardization is the suitable and proven basis for this.